데이터 사이언스 현재와 미래¶
데이터 사이언스 현재와 미래는 다음과 같이 달라질 것이다. 현재는 데이터 사이언스팀에서 경영진을 위해, 즉 의사결정을 지원하기 위한 보고서를 만드는 과정과 확정된 방안을 바탕으로 기술검토를 거쳐 데이터 사이언스 제품을 제작하는 과정이 주를 이루고 있지만, 앞으로 데이터 사이언스 개발팀에서 바로 데이터 사이언스 제품을 제작하는 과정으로 옮겨 나갈 것이다.
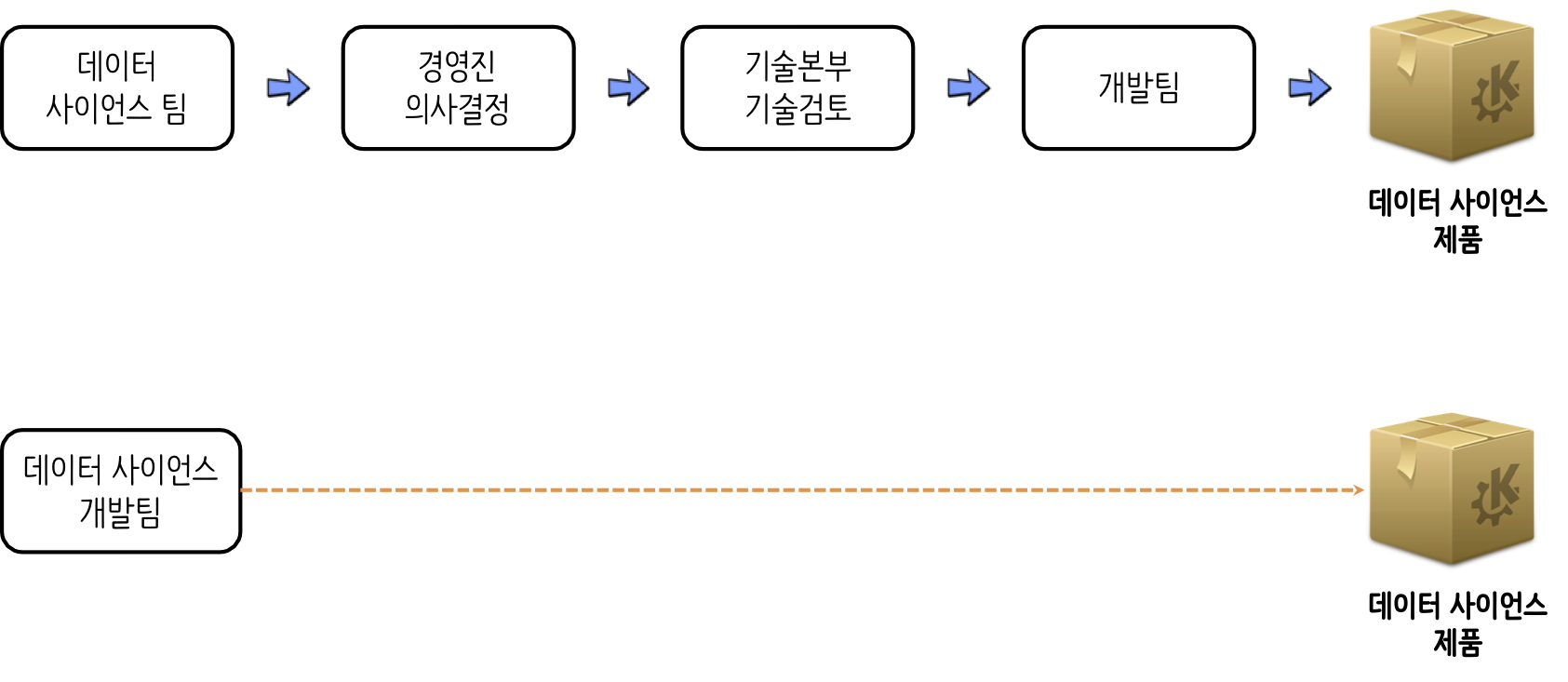
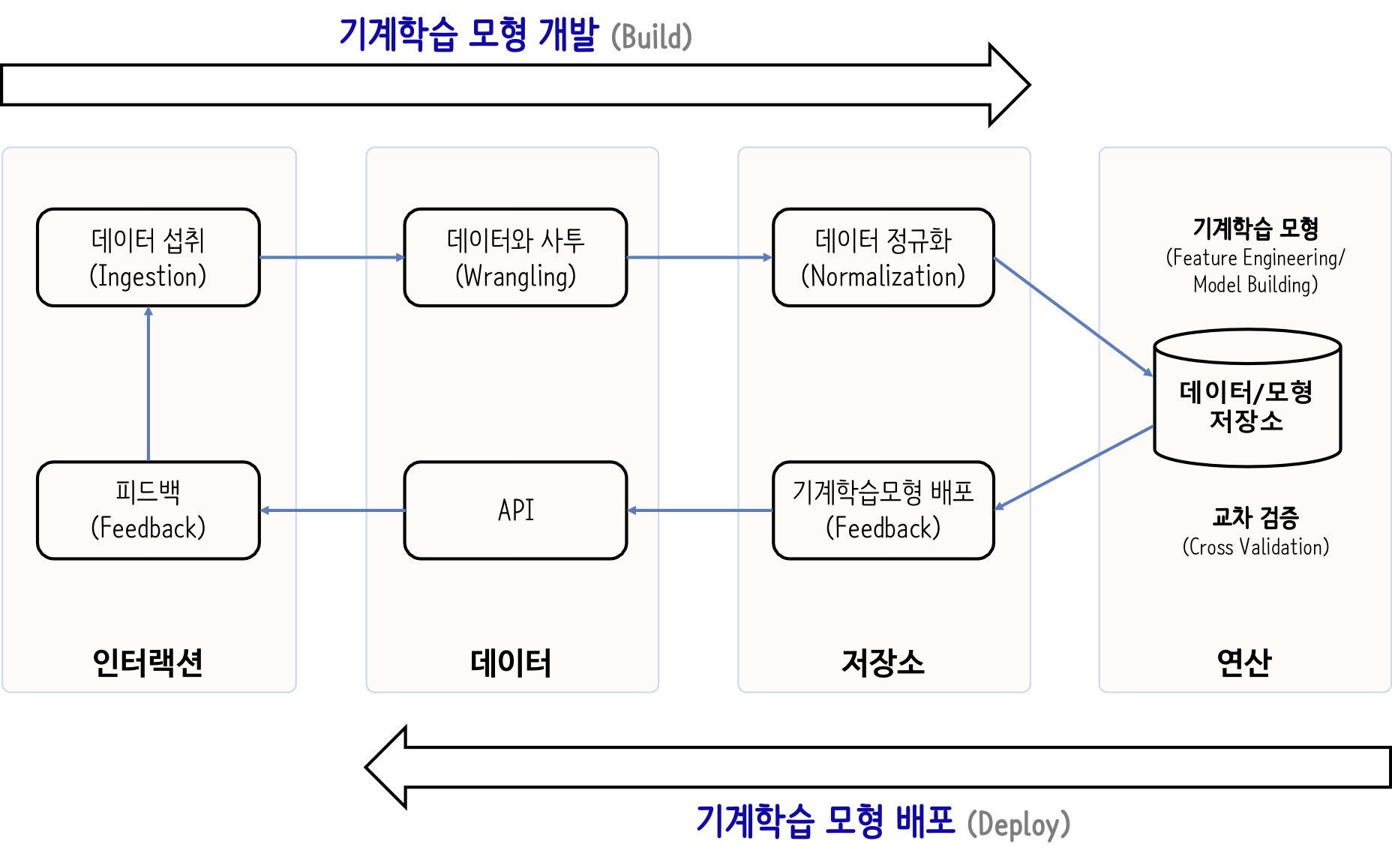
데이터 사이언스 제품 개발과정은 데이터 섭취(ingest)로부터 시작하여 기계학습 모형을 개발하고 이를 배포하여 API로 뽑아내는 과정을 아우른다.
텍스트 기술통계량¶
Neal Caren, "Using Python to see how the Times writes about men and women", University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill에 나온 내용을 바탕으로 간단한 모형을 제작해 보자.
텍스트 데이터¶
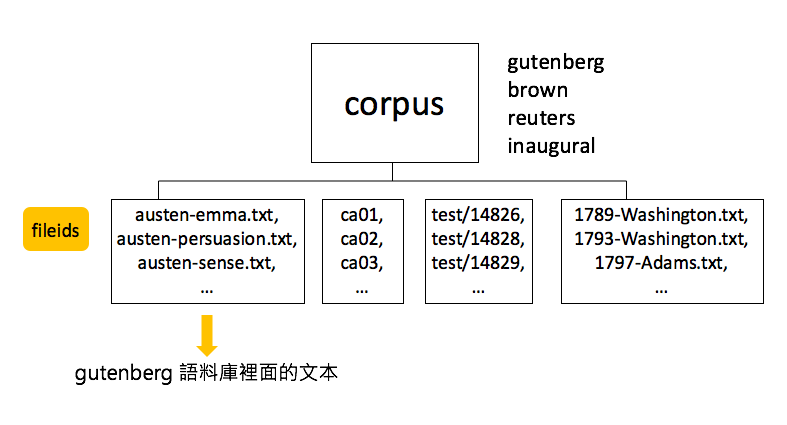
nltk 라이브러리에는 gutenberg, brown, reuters, inaugral 말뭉치(corpus)를 불러서 텍스트 자연어 처리 예제 데이터로 사용할 수 있다.
- corpus.raw(fileids)
- corpus.words(fileids)
- corpus.sents(fileids)
- corpus.categories()
- corpus.fileids()
가장 먼저 로이터 신문기사를 텍스트 데이터로 얻어보자. 이를 위해서 nltk 라이브러리에 포함된 nltk.download() 메쏘드를 사용해서 로이터 기사 데이터셋(reuters)을 가져온다.
그 다음 로이터 데이터셋에서 다양한 기사가 다양한 분류로 되어 있어 reuters.categories() 메쏘드를 사용해서 특정 영역 기사만 추출해낸다.
특정 영역(예를 들어 coffee) 내부에 뉴스기사가 많아, reuters.fileids("coffee") 명령어로 추출한 커피관련 뉴스 기사 하나만 추출해 낸다.
# import nltk
# nltk.download('reuters')
from nltk.corpus import reuters
## print(reuters.categories())
# ['acq', 'alum', 'barley', 'bop', 'carcass', 'castor-oil', 'cocoa', 'coconut', 'coconut-oil', 'coffee', 'copper',
# 'copra-cake', 'corn', 'cotton', 'cotton-oil', 'cpi', 'cpu', 'crude', 'dfl', 'dlr', 'dmk', 'earn', 'fuel', 'gas',
# 'gnp', 'gold', 'grain', 'groundnut', 'groundnut-oil', 'heat', 'hog', 'housing', 'income', 'instal-debt', 'interest',
# 'ipi', 'iron-steel', 'jet', 'jobs', 'l-cattle', 'lead', 'lei', 'lin-oil', 'livestock', 'lumber', 'meal-feed',
# 'money-fx', 'money-supply', 'naphtha', 'nat-gas', 'nickel', 'nkr', 'nzdlr', 'oat', 'oilseed', 'orange', 'palladium',
# 'palm-oil', 'palmkernel', 'pet-chem', 'platinum', 'potato', 'propane', 'rand', 'rape-oil', 'rapeseed', 'reserves',
# 'retail', 'rice', 'rubber', 'rye', 'ship', 'silver', 'sorghum', 'soy-meal', 'soy-oil', 'soybean', 'strategic-metal',
# 'sugar', 'sun-meal', 'sun-oil', 'sunseed', 'tea', 'tin', 'trade', 'veg-oil', 'wheat', 'wpi', 'yen', 'zinc']
coffee_docs = reuters.fileids("coffee")
print(reuters.raw(coffee_docs[0])[:1000])
## 남성/여성 정의
MALE = 'male'
FEMALE = 'female'
UNKNOWN = 'unknown'
BOTH = 'both'
MALE_WORDS = set([
'guy','spokesman','chairman',"men's",'men','him',"he's",'his',
'boy','boyfriend','boyfriends','boys','brother','brothers','dad',
'dads','dude','father','fathers','fiance','gentleman','gentlemen',
'god','grandfather','grandpa','grandson','groom','he','himself',
'husband','husbands','king','male','man','mr','nephew','nephews',
'priest','prince','son','sons','uncle','uncles','waiter','widower',
'widowers'
])
FEMALE_WORDS = set([
'heroine','spokeswoman','chairwoman',"women's",'actress','women',
"she's",'her','aunt','aunts','bride','daughter','daughters','female',
'fiancee','girl','girlfriend','girlfriends','girls','goddess',
'granddaughter','grandma','grandmother','herself','ladies','lady',
'lady','mom','moms','mother','mothers','mrs','ms','niece','nieces',
'priestess','princess','queens','she','sister','sisters','waitress',
'widow','widows','wife','wives','woman'
])
## 남성 혹은 여성 판별함수
def male_or_female(words):
mwlen = len(MALE_WORDS.intersection(words))
fwlen = len(FEMALE_WORDS.intersection(words))
if mwlen > 0 and fwlen == 0:
return MALE
elif mwlen == 0 and fwlen > 0:
return FEMALE
elif mwlen > 0 and fwlen > 0:
return BOTH
else:
return UNKNOWN
test_sentence = 'chairman'
# reuters.words(categories='coffee')
# ['INDONESIAN', 'COMMODITY', 'EXCHANGE', 'MAY', ...]
male_or_female(reuters.words(categories='coffee'))
문장 하나 이상 판정¶
앞서 male_or_female() 함수 하나를 가지고 판정을 했다면 문장을 넣어 문장별로 판정을 하는 로직을 count_gender() 함수로 작성하여 판정을 진행합니다.
from collections import Counter
def count_gender(sentences):
sents = Counter()
words = Counter()
for sentence in sentences:
gender = male_or_female(sentence)
sents[gender] += 1
words[gender] += len(sentence)
return sents, words
count_gender(reuters.words(categories='coffee'))
판정결과 출력¶
parse_gender() 함수를 작성하여 텍스트를 넣게 되면 이를 토큰화해서 객체를 만들고(sentences) 이를 계량화해서 출력하는 코드를 작성한다.
import nltk
def parse_gender(text):
sentences = [
[word.lower() for word in nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)]
for sentence in nltk.sent_tokenize(text)
]
sents, words = count_gender(sentences)
total = sum(words.values())
for gender, count in words.items():
pcnt = (count / total) * 100
num_sents = sents[gender]
print(f"{pcnt:.2f}% {gender} ({num_sents} sentences)")
parse_gender(reuters.raw(coffee_docs[0]))
텍스트 기술 통계량¶
한 문서에 대한 기술통계량에는 다음 사항이 포함된다.
- 전체 문단수 (paragraph)
- 전체 문장수 (sentence)
- 전체 단어수 (word)
- 유일무이한 단어수 (unique terms)
- 전체 단어에 대한 유일무이한 단어 비율 (lexical diversity) : $\frac{\text{유일무이한 단어수}}{{전체 단어수}}$
- 문단별 평균 단어수
- 총 처리시간
import nltk
reuters_words = reuters.words(categories='coffee')
fdist = nltk.FreqDist(w.lower() for w in reuters_words)
fdist.most_common(10)